IMF Raises Fresh Alarm Over Nigeria’s Rising Debt and Oil Dependence Urges Urgent Fiscal Reforms
The IMF has warned Nigeria over its rising debt and heavy reliance on oil revenue, urging urgent fiscal reforms, subsidy removal, and stronger revenue diversification to stabilize the economy.
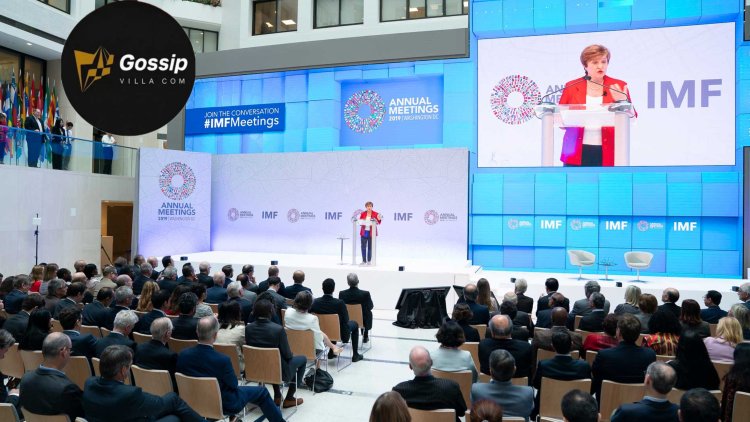

The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has issued a new warning to Nigeria, expressing concern over the country’s growing public debt and continued dependence on oil revenues to fund government operations.

This concern was raised during the World Bank and IMF Annual Meetings held in Washington D.C. earlier this week, where global financial experts and policymakers gathered to review economic developments across emerging markets.
IMF Flags Rising Debt Burden
According to the IMF, Nigeria’s public debt has increased significantly in recent years, with a growing portion of government earnings being used to service loans. The Fund cautioned that this trend poses a serious risk to the country’s fiscal stability and could limit its ability to fund essential sectors such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
Abebe Aemro Selassie, Director of the IMF’s African Department, noted that Nigeria’s economy has great potential but remains vulnerable to external shocks due to its reliance on crude oil exports.
“Nigeria needs to take urgent steps to diversify its revenue sources and strengthen domestic tax collection.
Sustained reforms are essential to secure fiscal stability and encourage investment,” Selassie said.
He further advised the government to phase out fuel subsidies, improve public financial management, and promote private-sector-led growth to reduce pressure on public finances.
Dependence on Oil and Market Risks
The IMF highlighted that crude oil still accounts for around 80% of Nigeria’s foreign exchange earnings and nearly half of government revenue. With global energy markets shifting toward renewables and oil prices fluctuating, this dependence leaves Nigeria vulnerable to external disruptions.
Economists argue that to secure long-term growth, Nigeria must accelerate diversification into non-oil sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology. Persistent inflation and exchange rate volatility have already made business operations difficult for many local and international investors.
Impact on Economy
Economic analysts warn that if Nigeria fails to implement meaningful reforms, debt servicing could soon consume most of the country’s revenue. However, they also note that the situation presents an opportunity for the government to re-strategize and build resilience.
By broadening the tax base, improving compliance through digital systems, and cutting wasteful expenditures, Nigeria could achieve sustainable economic recovery in the medium term.
IMF’s Key Recommendations
To strengthen the economy, the IMF recommended the following:
1. Eliminate fuel subsidies and redirect the funds toward infrastructure and social programs.
2. Diversify the economy by supporting manufacturing and agriculture.
3. Strengthen tax administration to improve domestic revenue generation.
4. Increase transparency and accountability in public spending.
5. Create a stable business environment to attract more foreign investments.
If these steps are taken, the IMF believes Nigeria can stabilize its economy and reduce its exposure to global oil market fluctuations.
Sources:
What's Your Reaction?